React State Management Tool: Redux
Concept: 状态提升 (Lifting State Up)
Definition: several components need to reflect the same changing data. We recommend lifting the shared state up to their closest common ancestor.
Example:
In React website, it gives an example. Fahrenheit & Centigrade
This data could be put in their shared parent component.
i.e., (if using class component)
class Calculator extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleCelsiusChange = this.handleCelsiusChange.bind(this);
this.handleFahrenheitChange = this.handleFahrenheitChange.bind(this);
this.state = {temperature: '', scale: 'c'}; }
handleCelsiusChange(temperature) {
this.setState({scale: 'c', temperature}); }
handleFahrenheitChange(temperature) {
this.setState({scale: 'f', temperature}); }
render() {
const scale = this.state.scale; const temperature = this.state.temperature; const celsius = scale === 'f' ? tryConvert(temperature, toCelsius) : temperature; const fahrenheit = scale === 'c' ? tryConvert(temperature, toFahrenheit) : temperature;
return (
<div>
<TemperatureInput
scale="c"
temperature={celsius} onTemperatureChange={this.handleCelsiusChange} /> <TemperatureInput
scale="f"
temperature={fahrenheit} onTemperatureChange={this.handleFahrenheitChange} /> <BoilingVerdict
celsius={parseFloat(celsius)} /> </div>
);
}
}Built-in Hooks
1) Context
- Can skip layers to pass data
- Similar to provide/inject in Vue
- Application: Change theme, change language
For example, we want to pass ThemeContext.
In parent component:
In child component:
then, we can directly use style
2) useReducer
Alternative solution of useState()
example:
However, when using reducer, parallel component might not be updated.
In this way, we can use Context in parent component to share reducer for its children components
In parent component write:
In child component write:
Then, can use all the data in child component
Redux
Why using Redux?
When the structure is complexed, it is hard to manage all the data and pass them using props
Therefore, it is necessary to use Redux.
React-Redux & Redux Toolkit
Install:
npm install @reduxjs/toolkit react-redux
Step:
1. create store folder under src
2. create index.ts
e.g.,
3. create count.ts (an example file, module name)
here, createSlice already uses immer under the hood, which allows us to operate on the state, for example:
4. Use Provider and store in index.tsx
5. In the page we want to use data, e.g., Count.tsx
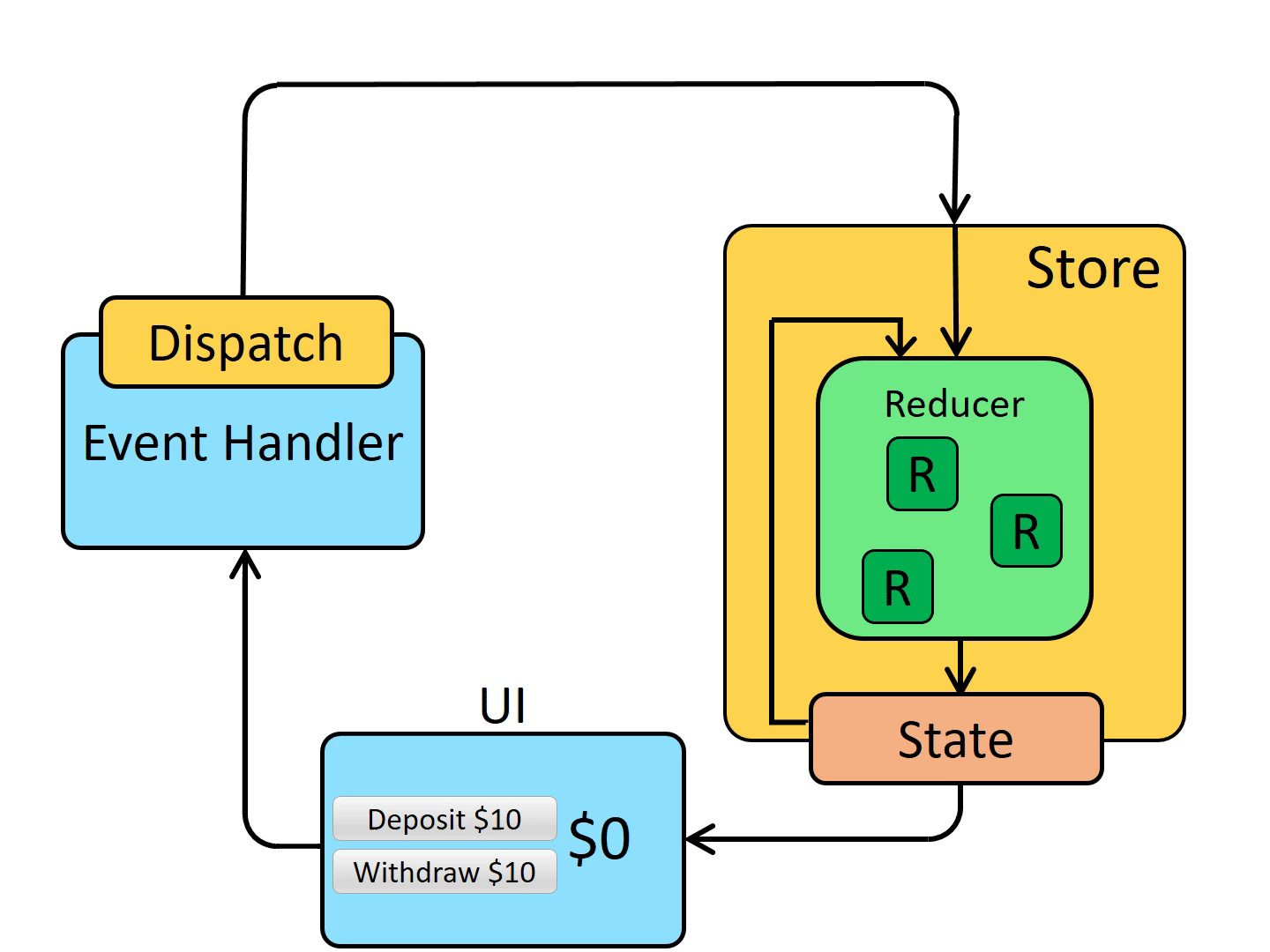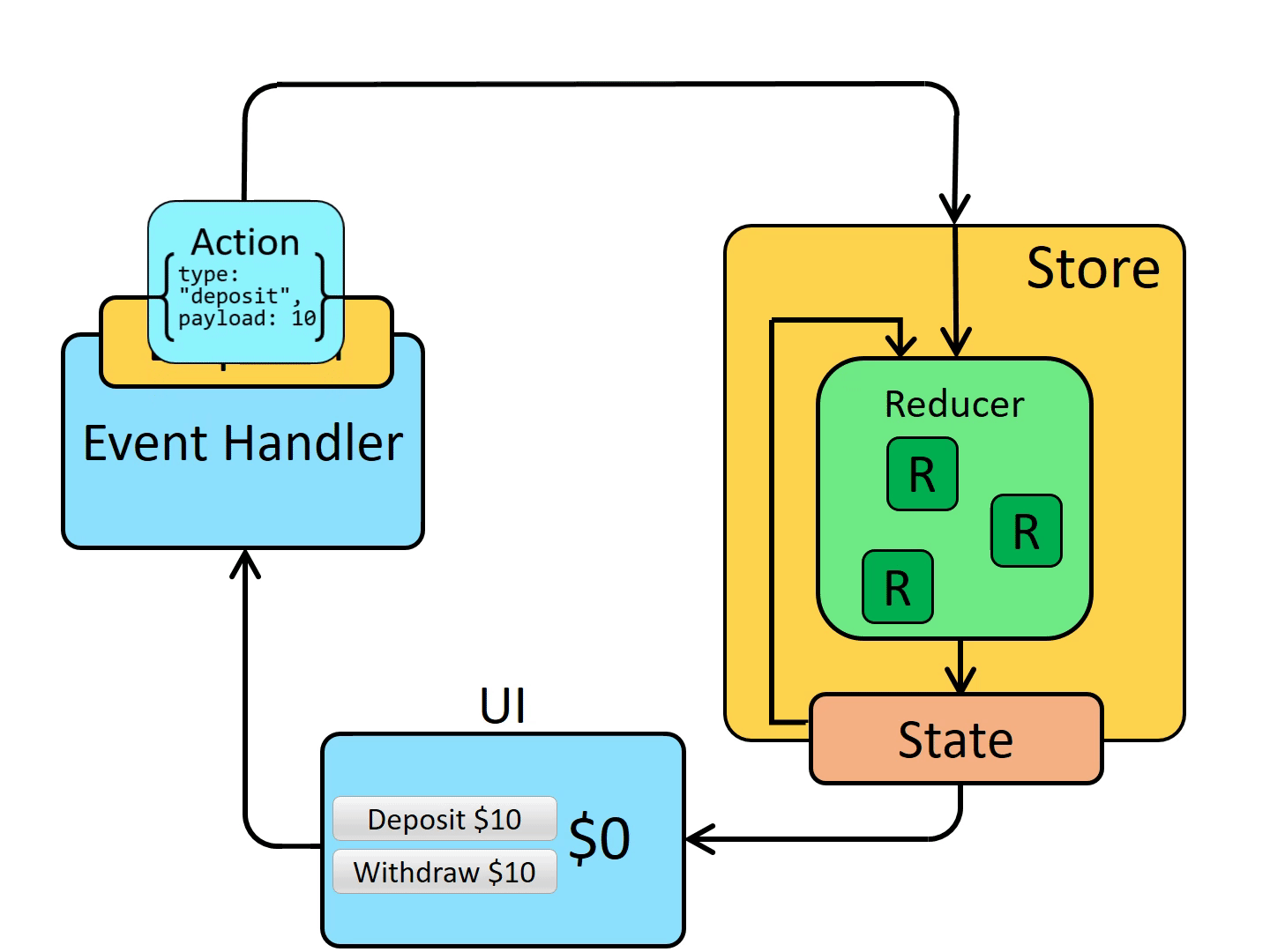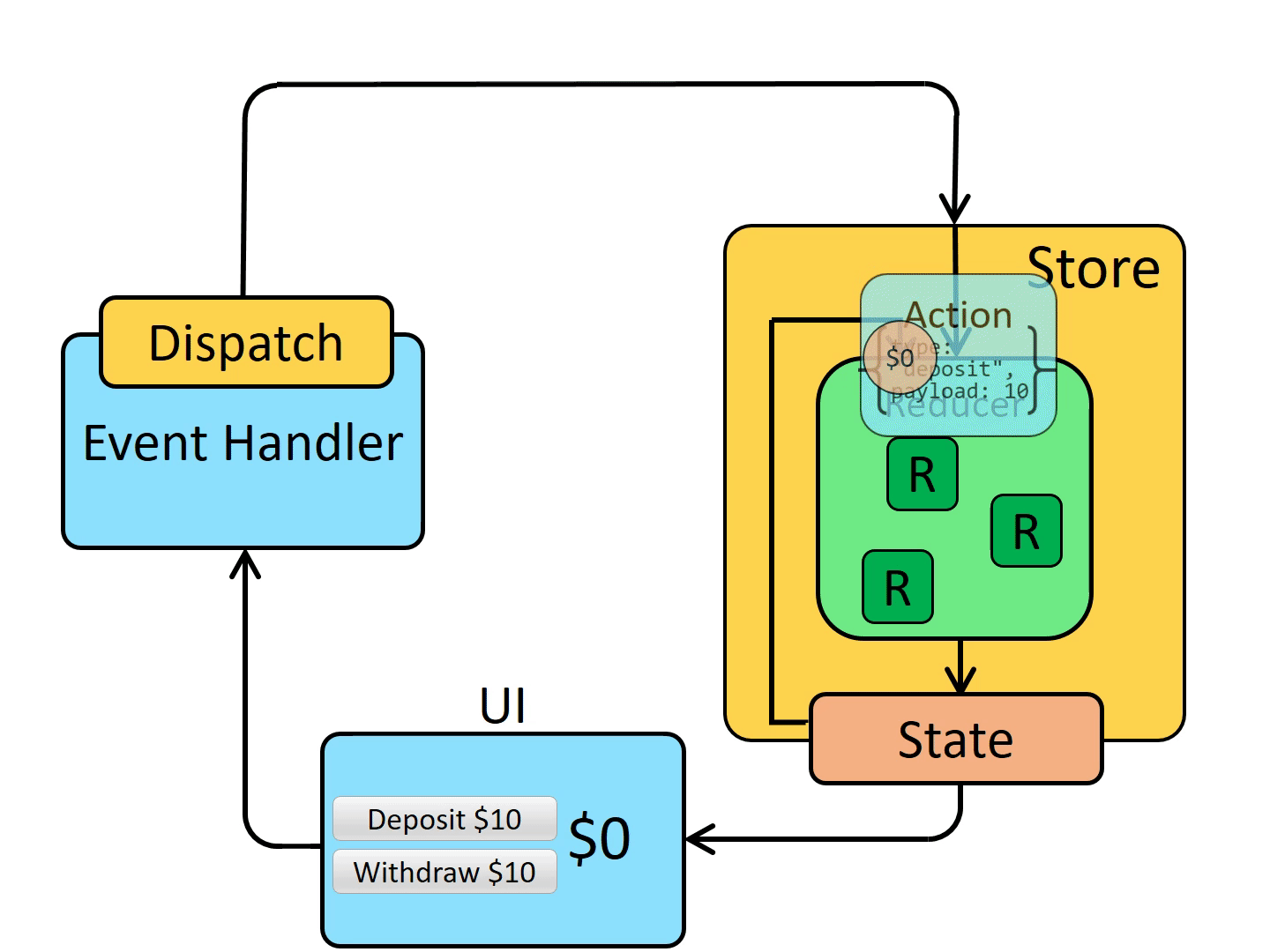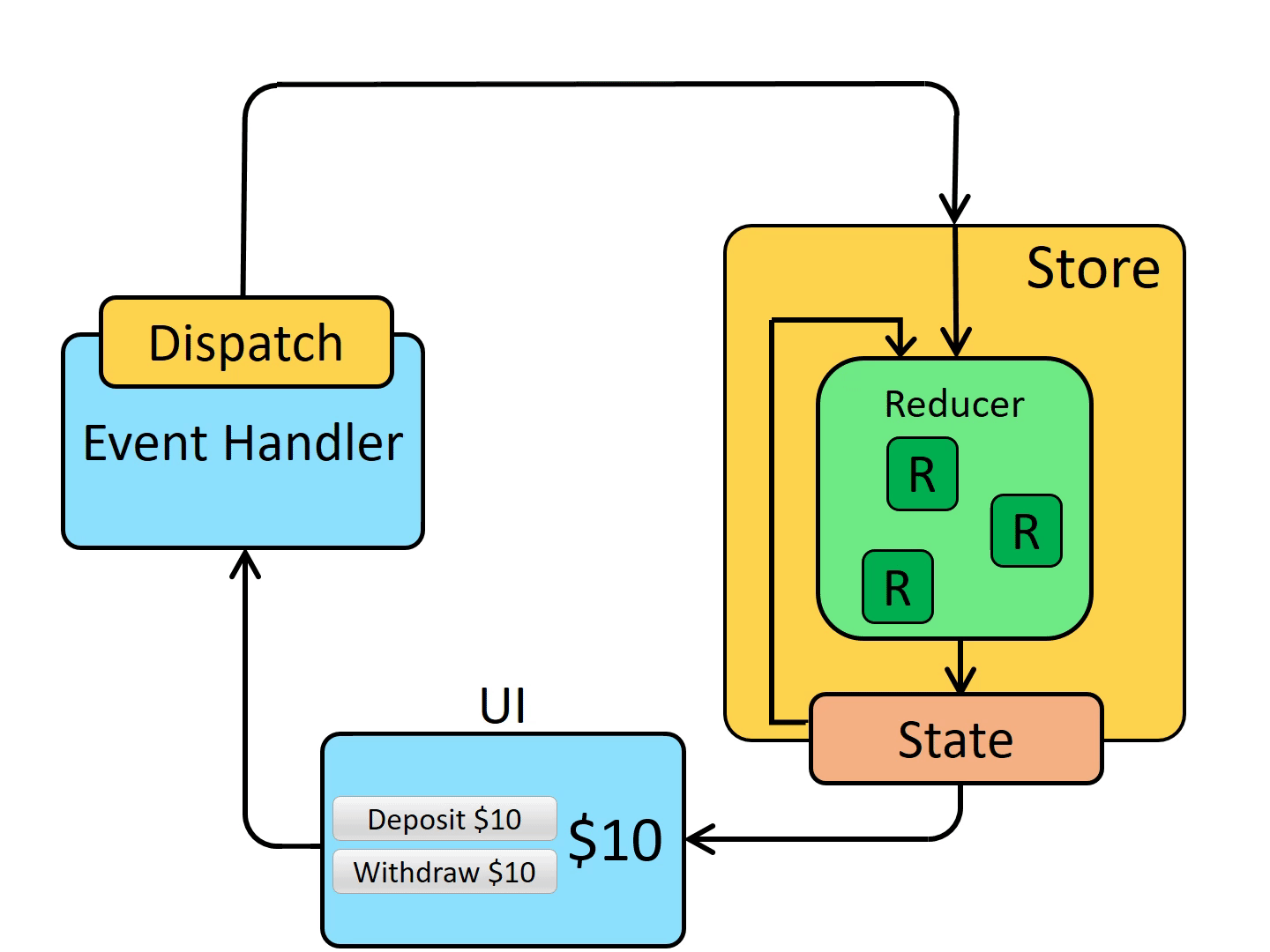
Redux 单向数据流 (one way data flow)
Store
当前 Redux 应用的状态存在于一个名为 store 的对象中。
store 是通过传入一个 reducer 来创建的,并且有一个名为 getState 的方法,它返回当前状态值:
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
const store = configureStore({ reducer: counterReducer })
console.log(store.getState())
// {value: 0}Dispatch
Redux store 有一个方法叫 dispatch。更新 state 的唯一方法是调用 store.dispatch() 并传入一个 action 对象。 store 将执行所有 reducer 函数并计算出更新后的 state,调用 getState() 可以获取新 state。
store.dispatch({ type: 'counter/incremented' })
console.log(store.getState())
// {value: 1}
dispatch 一个 action 可以形象的理解为 "触发一个事件"。发生了一些事情,我们希望 store 知道这件事。 Reducer 就像事件监听器一样,当它们收到关注的 action 后,它就会更新 state 作为响应。
Selectors
Selector 函数可以从 store 状态树中提取指定的片段。随着应用变得越来越大,会遇到应用程序的不同部分需要读取相同的数据,selector 可以避免重复这样的读取逻辑:
const selectCounterValue = state => state.value
const currentValue = selectCounterValue(store.getState())
console.log(currentValue)
// 2State 是只读的
更改状态的唯一方法是 dispatch 一个 action,这是一个描述所发生事件的对象。
这样,UI 就不会意外覆盖数据,并且更容易跟踪发生状态更新的原因。由于 actions 是普通的 JS 对象,因此可以记录、序列化、存储这些操作,并在以后重放这些操作以进行调试或测试。
使用 Reducer 纯函数进行更改
若要指定如何基于 action 更新状态树,请编写 reducer 函数。Reducers 是纯函数,它接收旧 state 和 action,并返回新 state。与任何其他函数一样,你可以将 Reducer 拆分为较小的函数以帮助完成工作,或者为常见任务编写可重用的 Reducer。
- Redux 的意图可以总结为三个原则
- 全局应用状态保存在单个 store 中
- store 中的 state 是只读的
- Reducer 函数用于更新状态以响应 actions
- Redux 使用“单向数据流”
- State 描述了应用程序在某个时间点的状态,UI 基于该状态渲染
- 当应用程序中发生某些事情时:
- UI dispatch 一个 action
- store 调用 reducer,随后根据发生的事情来更新 state
- store 通知 UI state 发生了变化
- UI 基于新 state 重新渲染
MobX: 声明式修改数据
State 数据
action 动作
derivation 派生: computed observer
Comments
Post a Comment